Introduction to Storage Tiering
Storage tiering has become a preferred solution to address business concerns associated with managing the exponential growth of data, cost, and application performance. The basic concept of storage tiering is to increase efficiency and decrease cost by categorizing data based on its value and how often it needs to be accessed. Once the access requirements for data types have been determined, the performance and cost efficiencies define what the most appropriate storage tier is for the data. The automated movement of data to different storage tiers based on its business value has traditionally been referred to as Information Lifecycle Management (ILM).
Storage tiering is rarely discussed among Tier-1 applications owners and infrastructure teams, even though they are essential to running a business as they tend to have Tier-1 as the only option. Tier-1 applications are designed, configured, and deployed to run on high-cost, high-performance storage devices.
After you migrate to the cloud or modern applications, the storage requirements for the data remaining in each application can change. You may still need to keep data for compliance reasons or for some other business purpose however, the need for fast retrieval is less. In most of these instances, cost and compliance replace high performance and speed requirements. In our experience, one of the biggest reasons people move data to an archive application is to reduce their cost of operations.
By way of example, data can be classified as follows:
- Mission Critical: Data in use on a high-performance application e.g., Transaction management.
- Hot: Data in constant use and high demand.
- Warm: Data used less frequently, but still must remain readily accessible.
- Cold: Data that must be retained but may never be accessed again.
Among these categories, hot, warm and cold are the most common classifications for decommissioning applications.
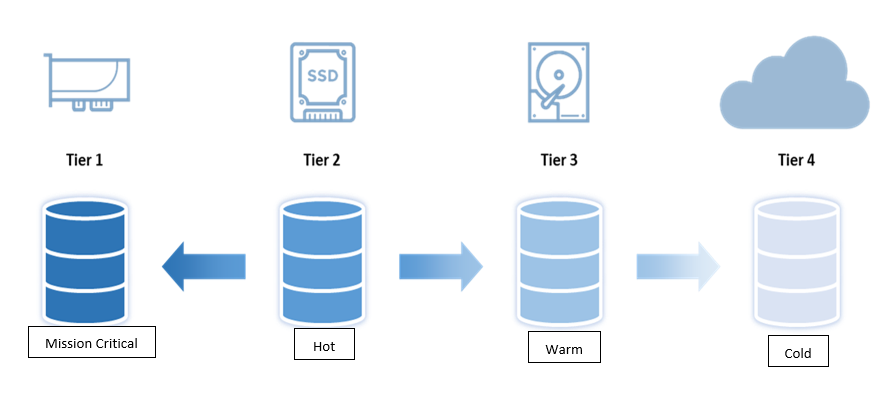
Data is stored on the storage mediums (tiers) based on the basic classification or values listed below:
| Features | Tier 0 | Tier 1 | Tier 2 | Tier 3 |
| Type of Data | Highly sensitive | Transactional support | Frequently accessed | Not frequently accessed |
| Access | Quick | Short delays | Very fast | Slow |
| Performance | High | High | Medium | Low |
| Example | Transaction data | High performance application | ERP/CRM system data | Compliant enterprise data |
| Cost | Relatively High | High | Medium | Very Low |
Features and characteristics of the classifications:
| Features | Mission Critical | Hot | Warm | Cold |
| Storage | Close to the moment of computation | Close to the moment of computation | On a remote server or private network | In cloud services |
| Access Speed | Very Fast | Fast | Medium | Slow |
| Pricing | High | High | Relatively high | Low |
| Storage Media | Flash | SSD | Cloud storage gateway or file server/NAS | Slower drives-tapes |
| Access Frequency | Very high | High | Relatively high | Low |
| Type of Data Stored | High-performance applications | Needed in daily business | Data not used in daily business | Data that is rarely accessed |
| Storage Tiers | Tier 0 | Tier 1 | Tier 2 | Tier 3 |
Storage Tiering Benefits
When considering archiving or retiring applications, one of the main drivers is cutting cost and simplifying operations. Implementing automatic movement of data (ILM) to warm, hot, and cold storage based on access, performance and value greatly benefits the application in the following ways:
Easy Disaster Recovery
The automated movement of data on storage tiers and archiving a production application can significantly reduce the costs and achieve a zero-recovery time objective (RTO) by reducing the amount of data the core system must recover during a disaster. In addition, it reduces back up times and reduces the amount of data volumes on tier 1 storage.
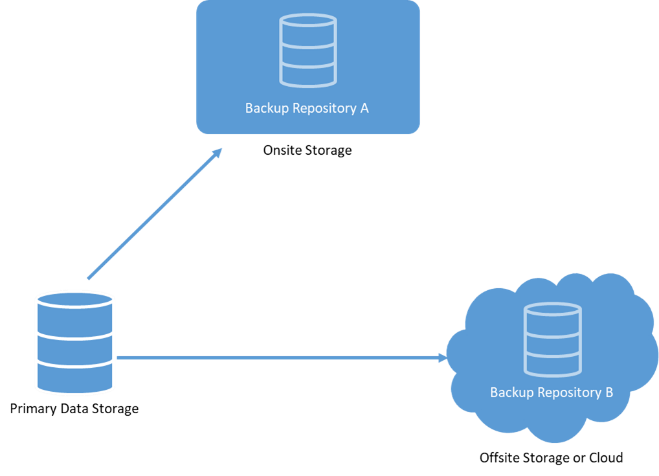
Controlled Data Management and Higher Storage Efficiency
Since data can be classified, categorized, and moved to different tiers systematically, the management and controls become easier at scale. In addition, tiered storage systems relieve the demand and stress on transactional systems by moving data that does not require such high performance to lower storage tiers or out of the application entirely.
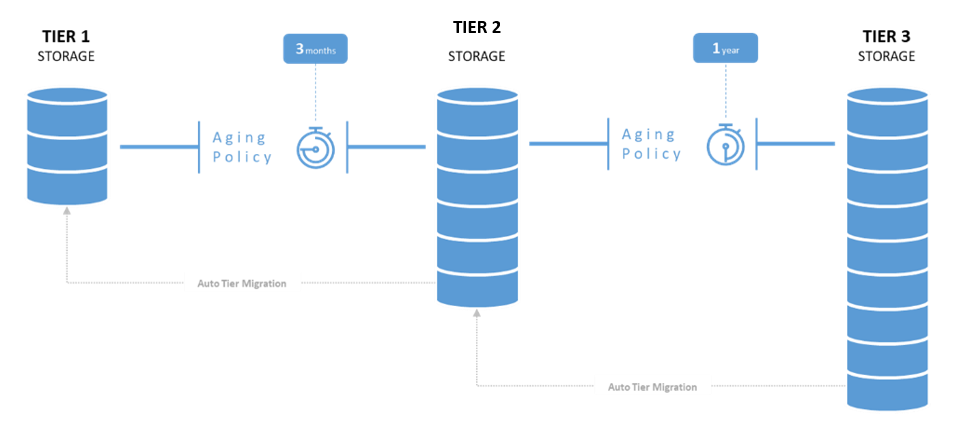
Reduced Data Storage and Backup Cost
Enterprise architects would agree that storage tiering for data cuts over 60% of the cost as it archives cold data to lower storage mediums. This process eliminates paying for unneeded high-performance storage for data that is of low value and low use. Reducing the tier 1 storage footprint improves your backup process and shortens the time it takes to complete.

Apart from these core benefits, the ability to automate storage tiering (ILM) across applications and data sets provides flexibility to use different storage systems, reduces the dependency of on-premise storage and allows flexibility in migrating data from source to target based on the business value and usage requirements.
Archon™, a Platform 3 Solutions *product, provides a comprehensive data management and ILM engine to help create a data aging strategy and enable decoupling of large unused datasets from the application, thus reducing cost and simplifying operations.
Conclusion
When transforming your business, incorporate a data aging strategy that allows you to categorize your data to provide greater flexibility in managing the movement and lifecycle based upon value, compliance, and access needs. The goal is to achieve the right balance between performance, cost containment and compliance. Storage tiering brings all these benefits in one place when building a data migration, archival and decommissioning strategy.
*The Platform 3 Archon™ Advantage
Platform 3 Solutions is a global leader in end-to-end legacy application solutions. We offer a full suite of products, services, and support to ensure a seamless transition from legacy technology to new and innovative platforms.
We deliver significant savings to free up cash, allowing for investment in innovation and development. Platform 3 assesses technology debt and formulates a plan to deliver an ROI through data migration, archival, and application decommissioning. With our proprietary tools and technology, we remove expensive and complicated end-of-life applications to simplify business operations and mitigate their risk profiles.
We manage legal and compliance risk by classifying your data to smartly migrate only what is valuable, archive what is needed for retention, and defensibly delete what is not needed.
Contact Platform 3 Solutions here to jumpstart your application retirement plan.

Board of Director, Chief Architect/Product Owner
Passionate about automating and solving complex problems with data for Fortune 500 clients. He has developed leading edge technology solutions to address the archival, decommissioning and migrating of legacy systems. Under his leadership, he has developed the Archon line of products and solutions to help clients in their open-source and digital transformation journeys.



